What are a formal letter and an informal letter?
A letter is a traditional form of communication between people, in which a sender writes a text and sends it to a receiver. The letters can be formal or informal according to their function and the relationship that exists between the sender and the receiver.
In a formal letter, the relationship between the two people is distant because it usually occurs between people who do not know each other personally. Formal language is used, then, and they are letters that usually have a predetermined structure. They can have labor, and commercial purposes, among others.
On the other hand, the informal letter is one in which both parts of the communication have an affective or close relationship. In this case, the issuer is allowed to choose the structure and elements of the letter, and informal language is usually used. They are written for various purposes such as invitations, greetings, and thanks, among others.
Comparison Chart
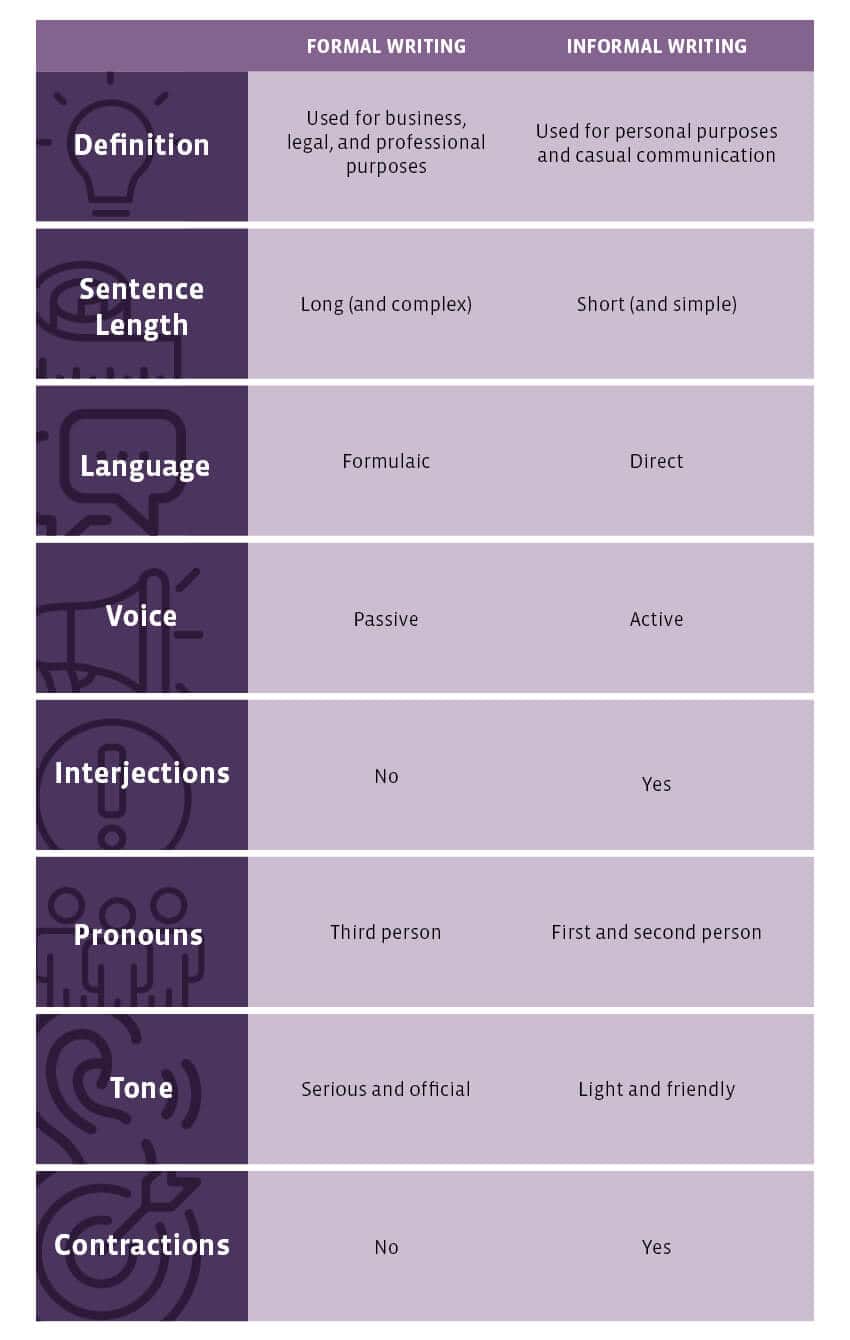
BASIS FOR COMPARISON |
FORMAL LETTER |
INFORMAL LETTER |
|---|---|---|
| Meaning | A formal letter is a letter, written in formal language, in the stipulated format, for official purposes. | A letter written in a friendly manner, to someone you are familiar with, is called an informal letter. |
| Objective | Professional Communication | Personal Communication |
| Format | Written in prescribed format only. | No prescribed format. |
| Written in first first first | First person – Business letters, third person – others. | First, second or third person. |
| Written business business business | Business, colleges/institutes, employers, organizations, etc. | Friends, family, acquaintances, etc. |
| Voice | Passive | Active |
| Sentences | Long and complex short-short-short | Short and simple |
| Size | Concise | Large or concise |
| Contractions and Abbreviations | Avoided | Used |
Definition of Formal Letters
A formal letter is any letter written in professional language, with a prescribed format for a formal purpose, i.e. it can be a recommendation letter, inquiry letter, complaint letter, cover letter, and so on. All business letters are formal, but vice versa is not possible. Such letters are used for a variety of reasons like a formal invitation, proposal, reference, making a complaint or inquiry, or applying for a job. While writing a formal letter one should keep in mind the following things:
- It should be in the specified format.
- It should avoid the use of unnecessary words.
- It should be straight to the point.
- It should be relevant and objective.
- It should be complex and thorough.
- It should be polite, even if it is a complaint letter.
- It should be free from any mistakes, i.e. grammatical or spelling.
There are three types of formal letters, i.e. business letters, letters for outlining civic problems, and job applications.
Definition of Informal Letters
An informal letter is a letter written to someone; we know fairly well. The letter can be used for some reasons like conveying messages, or news, giving advice, congratulating the recipient, requesting information, asking questions, etc. It is a personal letter, written to whom you are familiar, like friends, siblings, parents, or any other closed one. There is no specific format prescribed for writing this letter.
While writing an informal letter, one can afford to be friendly, and make use personal or emotional tone. Slang or colloquial terms, codes, abbreviations, etc. can also be used at the time of writing it, depending on the familiarity with the recipient.

Which Style is Appropriate?
Knowing the difference between formal and informal writing is only half the battle. The other important aspect is knowing which to use. Here are some examples of when you would use formal vs informal writing.
Use Formal Writing When:
- Writing professionally (reaching out to a client or prospect)
- Academic writings (essays, research papers, etc.)
- Job applications (resume writing, CVs, and cover letters)
- Reaching out to someone you do not know
Use Informal Writing When:
- Writing to a friend
- Sharing a story or writing a personal blog
- Writing creatively
- Instructed to do so (if in school)
- Writing dialogue and conversations
- Writing an outline
Transition Words For Writing A Letter

Formal writing tends to include the following:
- Long and complex sentences: Sentences tend to be compound and contain commas to link two ideas or use transitions like “Furthermore” and “To exemplify,”
- Does not use contractions: Would use “cannot” instead of “can’t”
- Objective: Do not offer personal opinions
- Doesn’t use colloquial language: You won’t see any slang or common everyday vocabulary
- Diverse vocabulary words: Vocabulary is of a higher level
- Use of subject-specific words: For example, if you are writing about biology, you’d use words like “epithelial cells” instead of “skin cells”
- Use of third person: Do not use first-person pronouns like “I” or “me”
Informal writing includes the following:
- Can use first person, second or third: You can use any type of pronoun, including “I”
- Can use slang: The use of everyday language and slang terms can be used, such as “It was cool that…”
- Active voice: Sentences tend to be written with a subject acting on the verb, such as “We chilled the drinks and went out to the sea” instead of “The drinks were chilled…”
- Personal emotional tone can be detected: Since the writing is personal, it can include feelings and the sharing of emotions
- Contraction and abbreviation: It’s okay to use “can’t” instead of “cannot” or “it’s” instead of “it is”
- Empathy: You can put yourself in the shoes of your audience and address their problems directly. This shows the author as coming from a place of understanding their situation.
