What Is a Conditional Sentence? (with Examples)
A conditional sentence is a sentence that gives a condition (e.g., If it snows) and the outcome of the condition occurring (e.g., the game will be canceled).
Easy Examples of Conditional Sentences
In each example below, the clause expressing the condition is highlighted.
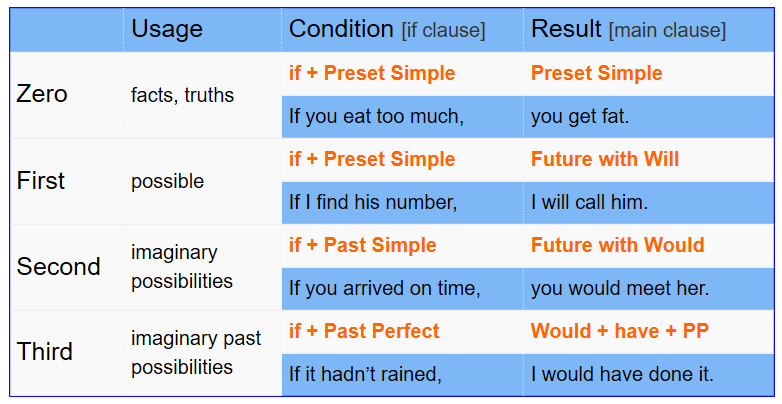
There are four types of conditional sentences:
| Type | Function | Example |
|---|---|---|
| zero conditional expresses | Expresses something as a fact if | If you sleep, you dream. |
| first conditional states | States the result of a possible future event occurring | If you get some sleep, you will feel better. The |
| second conditional states | States the result of an unlikely event occurring or an untruth being true if | If you became an insomniac, you would understand. (unlikely event occurring)
If you were an insomniac, you would understand. (untruth being true) |
| third conditional states states | States how the situation would be different with a different past if | If you had slept last night, you would have beaten your record. |
Some Real-Life Examples of Zero Conditional Sentences
A zero-conditional sentence expresses a general fact (i.e., a situation where one thing always causes another).
- If you rest, you rust. (Actress Helen Hayes)
- If you think you can, you can. And if you think you can’t, you are right. (Business magnate Henry Ford)
- You do ill if you praise, but you do worse if you censure, what you do not understand. (Polymath Leonardo da Vinci)
Structure: With a zero-conditional sentence, the simple present tense is used in both clauses. Also, the words if and when are interchangeable.
- If I make money, I’m happy. When I lose money, I’m happy. (Gambling magnate Lui Che Woo)
(With a zero-conditional sentence, the message is expressed as a fact. That doesn’t mean it’s true of course.)

Some Real-Life Examples of First Conditional Sentences
A first-conditional sentence states the result of a hypothetical, but possible, future event (e.g., If you rest) occurring.
- If one swain [young lover] scorns you, you will soon find another. (Roman poet Virgil)
- If I like food, even if it’s bad for me, I will eat it. (Reality TV star Kim Kardashian)
Structure: With a first-conditional sentence, the simple present tense is used in the if clause and the simple future tense is used in the main clause.

Some Real-Life Examples of Second Conditional Sentences
A second-conditional sentence states the result of an unlikely event occurring (e.g., If the boat sank) or an untruth being truth (e.g., If they were on time).
- If I won the lottery, I would still love you. I’d miss you, but I’d still love you. (Comedian Frank Carson)
- If I saw a heat wave, I would wave back. (Comedian Steven Wright)
- If I had any humility, I would be perfect. (Media mogul Ted Turner)
- If you set out to be liked, you would compromise on everything and achieve nothing. (Margaret Thatcher)
Structure: With a second-conditional sentence, the simple past tense is used in the if-clause, and would (rarely should or could) with the base form of a verb is used in the main clause.

Some Real-Life Examples of Third Conditional Sentences
Third-conditional sentences express how the situation would be different if the past had been different.
- If my lawyer and I had communicated properly in January 1958, this whole history would have been entirely different. (Inventor of the laser Gordon Gould, who fought unsuccessfully to patent it)
- If I had learned education, I would not have had time to learn anything else. (Business magnate Cornelius Vanderbilt)
- If I had known how hard it would be to do something new in the payments industry, I would never have started PayPal. (Co-founder of PayPal Peter Thiel)
With a third-conditional sentence, the past perfect tense is used in the if-clause, and would have (rarely could have) with a past participle is used in the main clause.

More about Conditional Sentences
If-clauses without an If. An if-clause can be introduced with other terms such as when, unless, provided that and as long as or by using inversion (e.g., Were he available, he would be selected.)
- I will swim unless the water is too cold.
- I will swim as long as the water is not too cold.
- I will swim provided that the water is not too cold.
When they introduce an if-clause, when, provided that , and as long as can usually be replaced with if. Also, unless could be replaced with an if..not construction (e.g., if the water is not too cold). So, the term if-clause, despite being disliked by some grammarians, is pretty accurate. It’s certainly convenient.
Mixed Conditionals. Occasionally, a conditional sentence will “steal” the structures from two different types of conditional sentences. This most commonly occurs with a conditional sentence that uses the structure of a second-conditional sentence for one clause and the structure of a third-conditional sentence for the other. These are called mixed conditionals.
- If we were smarter, we wouldn’t have set off in this weather.
- If you had checked the weather, we wouldn’t be stranded now.
(The if-clause is a second-conditional structure. The main is the third-conditional structure.)
(The if-clause is a third-conditional structure. The main is the second-conditional structure.)

