Nervous System
It is divided into two main components:
- The central nervous system (CNS)
- The peripheral nervous system (PNS)
Central Nervous System (CNS)
- It serves as the main control center for the entire body, processing information and sending signals to various parts of the body.
- The CNS is the core of the nervous system and consists of two primary components: the brain and the spinal cord.
Brain
The brain is the control center of the nervous system and the body. It processes information, interprets sensory input, initiates responses, and stores and retrieves information. Brain responsible for processing information, initiating responses, and regulating bodily functions. It is involved in consciousness, memory, emotions, and decision-making.
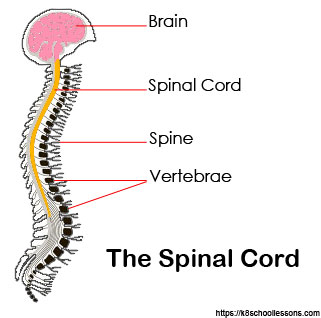
Spinal Cord
The spinal cord is a long, thin, tubular structure that runs from the base of the brain down the spine. It serves as a communication pathway between the brain and the rest of the body, as well as a reflex center. Reflexes are rapid, involuntary responses to stimuli. It serves as a relay and information-processing center, connecting the brain to the rest of the body. .
Key functions of the CNS include
- Processing sensory information from the PNS.
- Initiating voluntary and involuntary responses.
- Controlling thoughts, emotions, and consciousness.
- Housing and protecting delicate neural tissue.
Peripheral Nervous System (PNS):
- The PNS encompasses all neural structures outside the CNS and serves as a communication system between the CNS and the rest of the body.
-
The peripheral nervous system includes all nervous tissue outside the CNS.
-
It connects the CNS to the rest of the body, including muscles, organs, and sensory receptors.
- It can be further divided into two main subdivisions: the somatic nervous system (SNS) and the autonomic nervous system (ANS).
Somatic Nervous System (SNS)
- The somatic nervous system controls voluntary muscle movements and sensory perception.
- It enables conscious control over skeletal muscles, allowing you to move and interact with the environment.
- Sensory neurons transmit information about touch, pain, temperature, and position from the body to the CNS.
Key functions include
- Transmitting sensory information (e.g., touch, pain, temperature) from the body’s sensory receptors (such as the skin) to the CNS.
- Transmitting motor commands from the CNS to skeletal muscles, enabling voluntary movements.
- It allows you to consciously interact with the environment, such as moving your limbs and feeling sensations.
Autonomic Nervous System (ANS)
- The autonomic nervous system regulates involuntary bodily functions, such as heart rate, digestion, and breathing.
It is divided into two branches:
1- Sympathetic Nervous System
- Activated during the “fight or flight” response, which prepares the body for action.
- Increases heart rate, dilates airways, redirects blood flow to muscles, and triggers various stress responses.
- Helps the body respond to emergencies and threats.
2- Parasympathetic Nervous System:
- Responsible for “rest and digest” activities, it slows heart rate, aids in digestion, and promotes relaxation and conserve energy.
- Slows heart rate, stimulates digestion, and reduces stress responses.
- Allows the body to recover and maintain a balanced internal environment.
