Types of Wave Motion
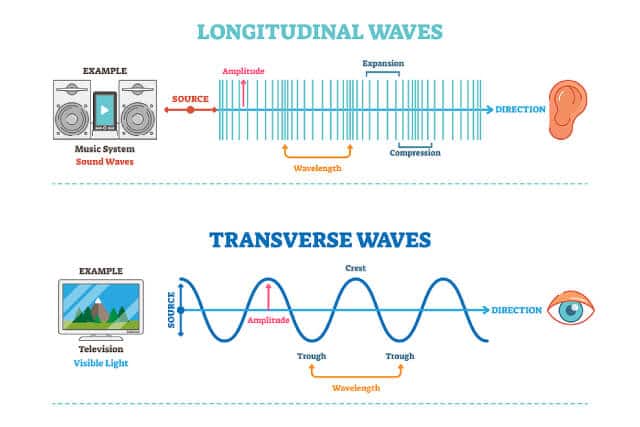
- Wave motion can be classified into two main types: transverse waves and longitudinal waves.
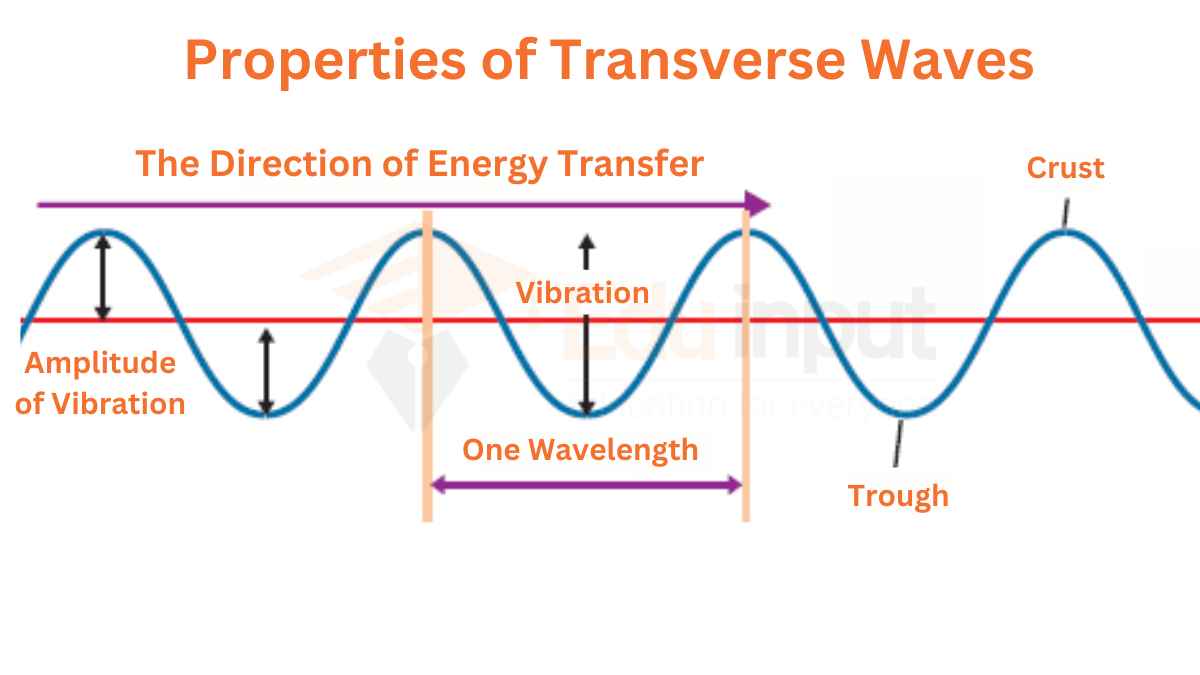
- Transverse waves are waves in which the particles of the medium vibrate perpendicular to the direction of the wave’s travel. Examples of transverse waves include water waves and light waves.
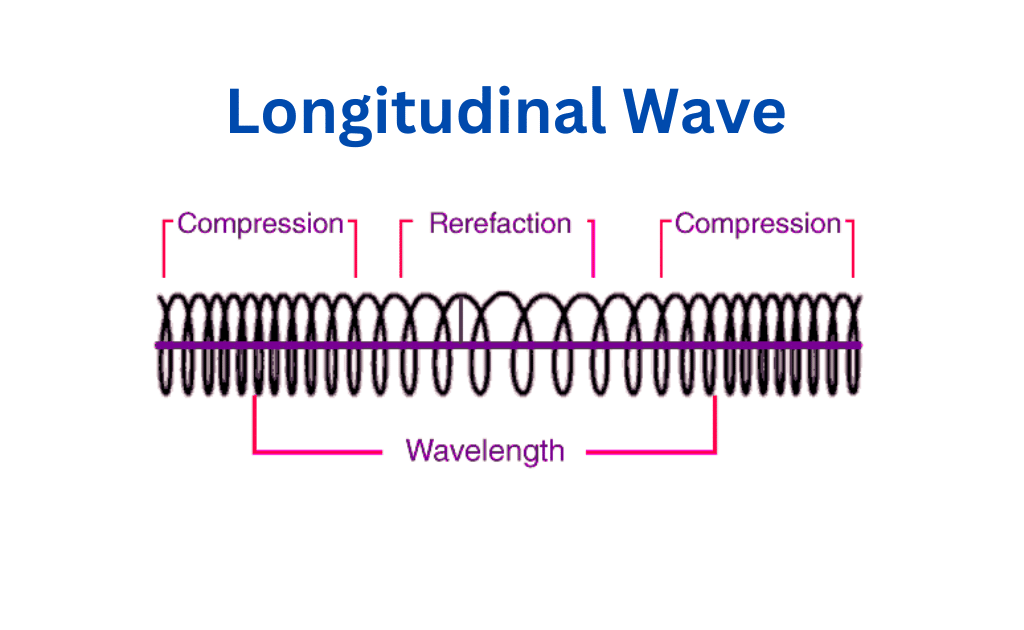
- Longitudinal waves are waves in which the particles of the medium vibrate parallel to the direction of the wave’s travel. Examples of longitudinal waves include sound waves and seismic waves.
Transverse waves
To understand transverse waves, consider a slinky spring lying on a smooth table. If you move one end of the slinky up and down, the wave will travel through the slinky in a direction perpendicular to the direction of the up-and-down motion. The particles of the slinky will vibrate perpendicular to the direction of wave travel.
Transverse waves can also be observed on the surface of water in a pond or a ripple tank. If you drop a stone into a pond, the waves that travel outward will be transverse waves. The water particles will vibrate up and down, perpendicular to the direction of wave travel.
Longitudinal waves
To understand longitudinal waves, consider the same slinky spring lying on a smooth table. If you push and pull one end of the slinky, the wave will travel through the slinky in the same direction as the push-and-pull motion. The particles of the slinky will vibrate parallel to the direction of wave travel.
Sound waves are another example of longitudinal waves. Sound waves are created when the particles of a medium vibrate back and forth. The particles of the medium vibrate parallel to the direction of wave travel.