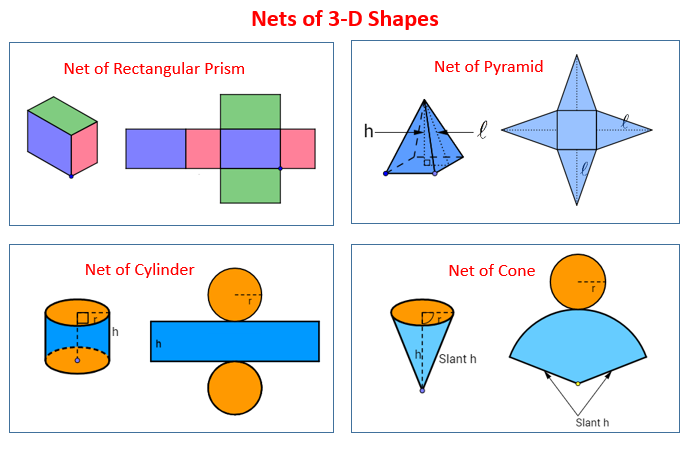
What are Three-Dimensional Shapes?
Shapes that can be measured in 3 directions are called three-dimensional shapes. These shapes are also called solids. Length, width, and height (or depth or thickness) are the three measurements of three-dimensional shapes. These are the part of three-dimensional geometry.
They are different from 2D shapes because they have thickness. Several examples can be found in everyday life. Some of them are:
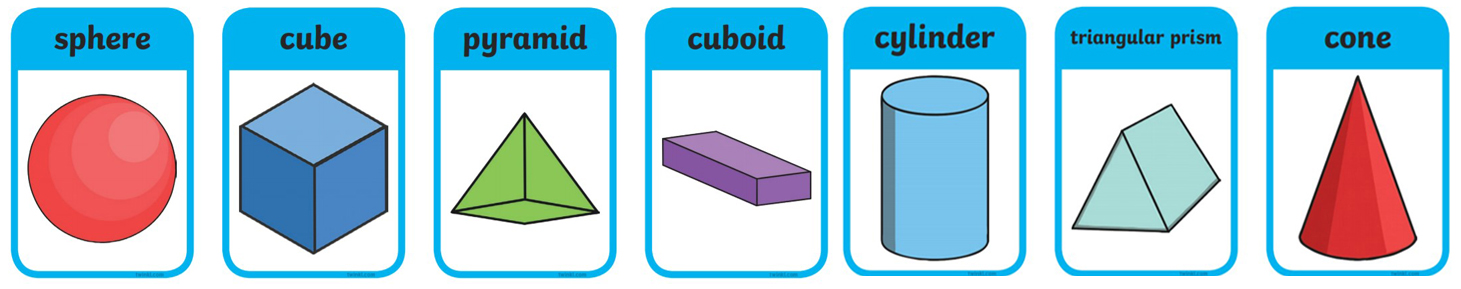
Solid Shapes in Maths
In Mathematics, the three-dimensional objects having depth, width and height are called solid shapes. Let us consider a few shapes to learn about them. You can find many examples of solid shapes around you, such as a mobile, notebook or almost everything you can see around is a solid shape.
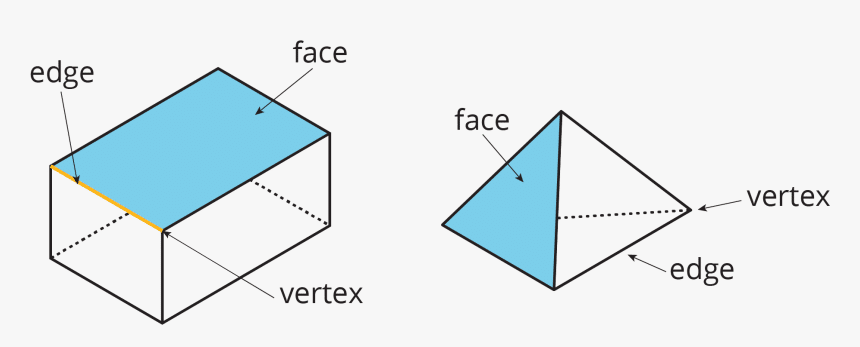
Faces, Edges, and Vertices of Three Dimensional Shapes
Three-dimensional shapes have many attributes, such as vertices, faces, and edges. The flat surfaces of the 3D shapes are called faces. The line segment where two faces meet is called an edge. A vertex is a point where three edges meet.
List of Three-dimensional Shapes
The list of three-dimensional shapes are as follows:
- Cube: A cube is a solid or three-dimensional shape which has 6 square faces. The cube has the following properties.
- All edges are equal
- 8 vertices
- 12 edges
- 6 faces
- Cuboid: A cuboid is also called a rectangular prism, where the faces of the cuboid are a rectangle in shape. All the angles measure 90 degrees. The cuboid has
- 8 vertices
- 12 edges
- 6 faces
-
Prism: A prism is a 3D shape which consists of two equal ends, flat surfaces or faces, and also has identical cross-section across its length. Since the cross-section looks like a triangle, the prism is generally called a triangular prism. The prism does not have any curve. Also, a prism has
- 6 vertices
- 9 edges
- 5 faces – 2 triangles and 3 rectangles
-
Pyramid: A pyramid a solid shape, whose outer faces are triangular and meet to a single point on the top. The pyramid base can be of any shape such as triangular, square, quadrilateral or in the shape of any polygon. The most commonly used type of a pyramid is the square pyramid, i.e., it has a square base and four triangular faces. Consider a square pyramid, it has
- 5 vertices
- 8 edges
- 5 faces
-
Cylinder: A cylinder is defined as a three-dimensional geometrical figure which has two circular bases connected by a curved surface. A cylinder has
- No vertex
- 2 edges
- 2 flat faces – circles
- 1 curved face
-
Cone: A cone is a three-dimensional object or solid, which has a circular base and has a single vertex. The cone is a geometrical figure that decreases smoothly from the circular flat base to the top point called the apex. A cone has
- 1 vertex
- 1 edge
- 1 flat face – circle
- 1 curved face
-
Sphere: A sphere is a three-dimensional solid figure which is perfectly round in shapes and every point on its surface is equidistant from the point is called the center. The fixed distance from the center of the sphere is called a radius of the sphere. A sphere has
- No vertex
- No edges
- 1 curved face