Compound Shape
A compound shape (or composite shape) is any shape which is made up of two or more shapes. They are often rectilinear shapes which have straight sides and right angles.
What is the perimeter of compound shapes?
The perimeter of compound shapes is the distance around a compound shape. The perimeter of a shape is finding the total distance around the outside of a 2D shape.
For example, Find the perimeter of this compound shape.
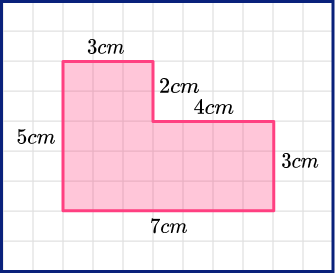
To find the perimeter we add all the lengths of the sides.
The perimeter is
How to calculate the perimeter of compound shapes?
In order to calculate the perimeter of the compound shape:
- Work out any missing lengths.
- Add all the side lengths.
- Write the final answer with the correct units.
Example
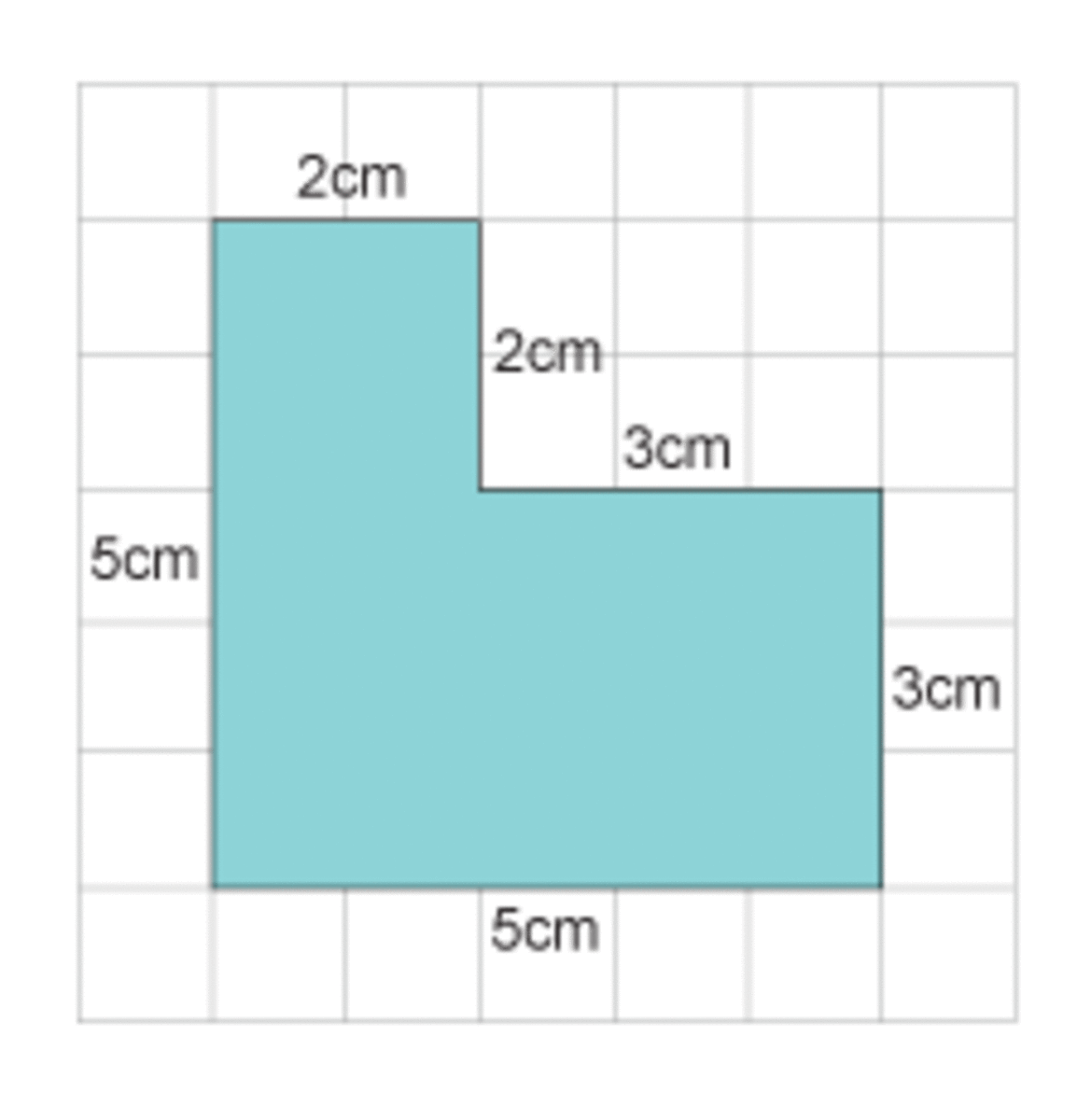
In this example you need to add up all the sides:
5 + 5 + 3 + 3 + 2 + 2 = 20 cm
(Note, it is a good idea to cross off each length as you go along, so you make sure you count all the sides and also that you do not add a length twice. This is because compound shapes can become very complicated so you can add up a lot more sides than the example given here.)
Common Misconceptions
- Order of adding the sides
The addition is commutative. This means it doesn’t matter what order the sides of the shape are added in.
- Check the units
Check which units are involved in the question as there may be a mixture.