Math Lab Activity
– Magic Squares
Magic squares have been popular math puzzles for over 3,000 years, and once were thought to have mystical powers.
Follow these simple rules to complete your own magic square:
- Use each number only once.
- Each row, column, and diagonal must add up to the same answer.
Fun Fact
Historical Squares – Over 3,000 years ago, ancient Chinese included magic squares in their mystical writings. Magic squares also appeared in art. For instance, Albrecht Dürer’s famous engraving of Melancholia (1514) includes a picture of a magic square.
Procedure:
- For this first magic square, use the numbers from 1 to 9.
HINT: Each column, row, and diagonal adds up to 15.
- Try again, but this time use only the EVEN numbers from 2 to 16 (2, 4, 6, and so forth).
HINT: Each column, row, and diagonal adds up to 30.
- Try again, but this time use only the ODD numbers from 1 to 17 (1, 3, 5, and so forth).
HINT: Each column, row, and diagonal adds up to 27.
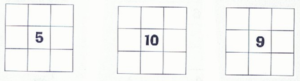
- Now, let’s make things more difficult. In the following magic square, some of the numbers are negative-you need to use every number from -4 to 4.
HINT: Each column, row, and diagonal adds up to 0.
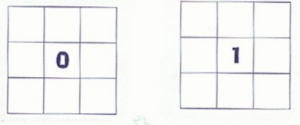
- Here is another magic square. This time, use the numbers from 3 to 5.
HINT: Each column, row, and diagonal adds up to 3.
So, now you think you are a magic square pro? Not so fast!
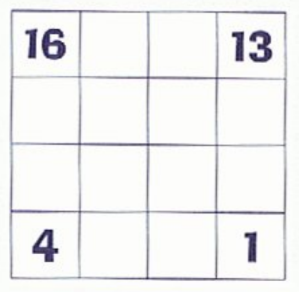
Let’s make the magic square larger and see if you can still solve the puzzle. For the following square, use the numbers from 1 to 16.
HINT: Each column, row, and diagonal adds up to 34.
How Big Can You Go?
If you think the 4-by-4 square is hard, you’ll really be impressed by Ben Franklin, a scientist, inventor, statesman, printer, philosopher, musician, and economist (a jack of all trades!), famous for flying a kite during a lightning storm. In addition to all his other jobs and hobbies, Ben liked to solve math puzzles. One of his mathematical achievements was to solve an 8-by-8 and 16-by-16 magic square.
Visit www.pasles.org/ Franklin.html to take a closer look at Ben’s magic squares.