About Lesson
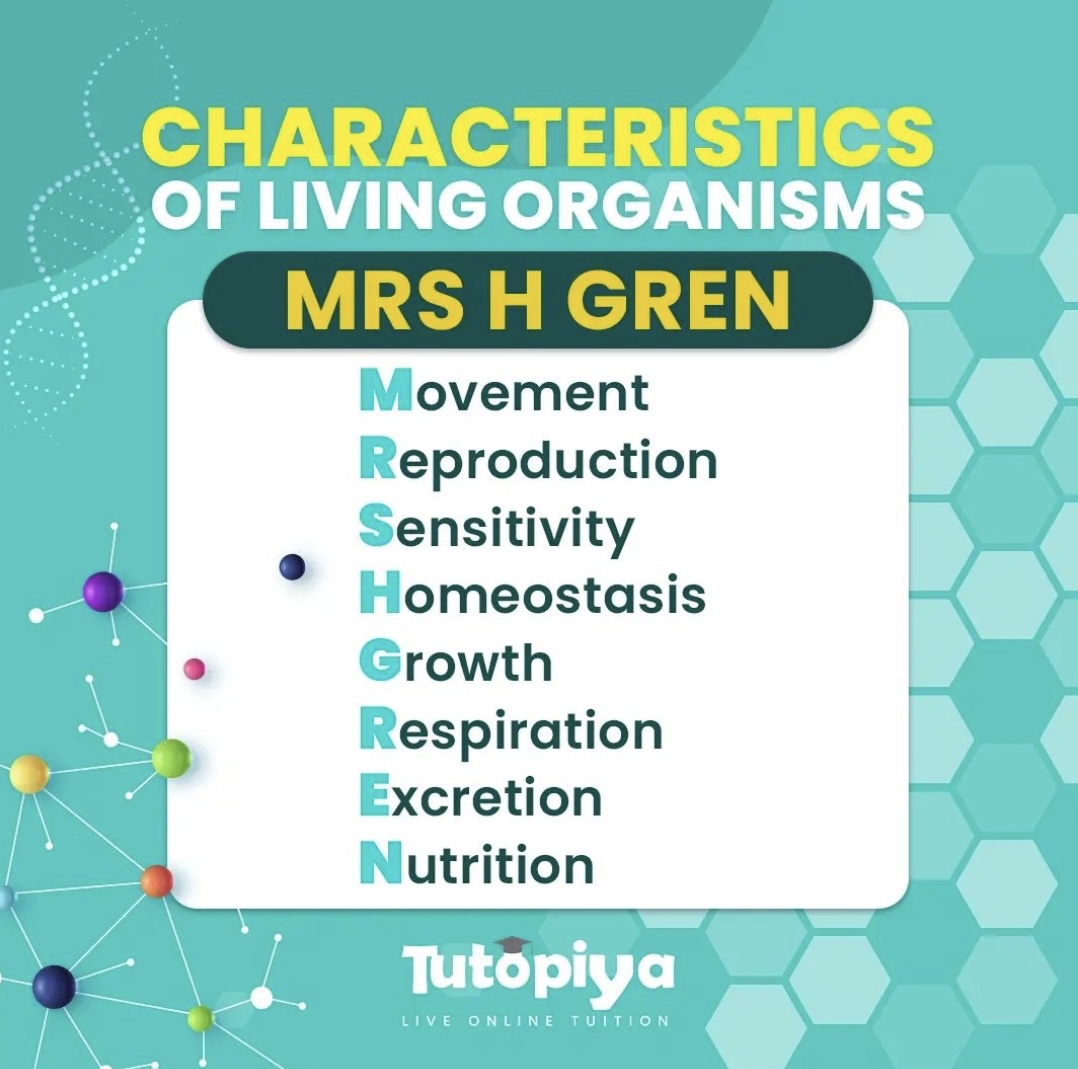
Characteristics of living organisms
- Movement: Living organisms can move from one place to another. They can also move parts of their bodies, such as their legs, arms, and wings.
- Respiration: Living organisms respire, which means they take in oxygen from the environment and release carbon dioxide.
- Sensitivity: Living organisms can sense their environment and respond to changes in it. For example, they can sense light, temperature, and sound.
- Growth: Living organisms grow over time. They can increase their size and number of cells.
- Reproduction: Living organisms can reproduce, which means they can create new individuals of their own kind.
- Excretion: Living organisms excrete waste products, which are substances that their bodies don’t need.
- Nutrition: Living organisms need to eat food to get the energy they need to grow, reproduce, and maintain their bodily functions.
These characteristics are all essential for life. Without them, an organism would not be able to survive and reproduce.

Some examples of how these characteristics are expressed in different living organisms
- Movement: Animals can move from one place to another by walking, running, swimming, or flying. Plants can move their leaves and flowers towards the sun.
- Respiration: Animals breathe through their lungs, skin, or gills. Plants breathe through their leaves and stems.
- Sensitivity: Animals can sense their environment through their eyes, ears, nose, tongue, and skin. Plants can sense light, gravity, and water.
- Growth: Animals grow by increasing the size and number of their cells. Plants grow by increasing the size and number of their cells, as well as by adding new tissues and organs.
- Reproduction: Animals reproduce sexually or asexually. Plants can reproduce sexually or asexually, or by vegetative propagation.
- Excretion: Animals excrete waste products through their urine, feces, and sweat. Plants excrete waste products through their leaves and stems.
- Nutrition: Animals eat other animals or plants. Plants get their energy from the sun through photosynthesis.
Exercise Files