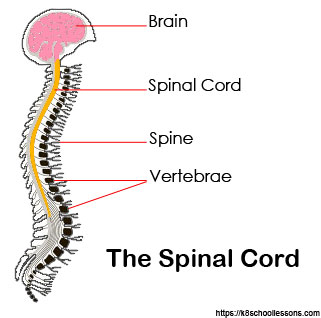
Animals constantly use their senses to gather information about their surroundings. Nerves in the body pick up this information. In most animals the nerves send the information to the brain or a similar organ. The brain makes sense of the information. It then sends a message back through the nerves to tell the body how to react. This network of nerves and brain is called the nervous system.

In mammals and other animals with backbones the brain and the spinal cord form the central part of the nervous system. The spinal cord is a long bundle of major nerves. It runs from the brain down an animal’s back. Nerves throughout the body carry information to and from the central nervous system.
The nerve cells, or neurons, are the basic units of the nervous system. The human body contains billions of neurons. More than 10 billion neurons make up the brain.
Neurons have a nucleus, or center, and two or more long fibers, or threads. Impulses travel to and from the neurons along these fibers.
Neurons are not able to reproduce as some other cells do. They cannot divide themselves to create more neurons. Neurons in most of the body can regrow if they are slightly damaged. However, neurons in the brain and spinal cord cannot regrow at all. This is why severe damage to the brain or the spinal cord is permanent.
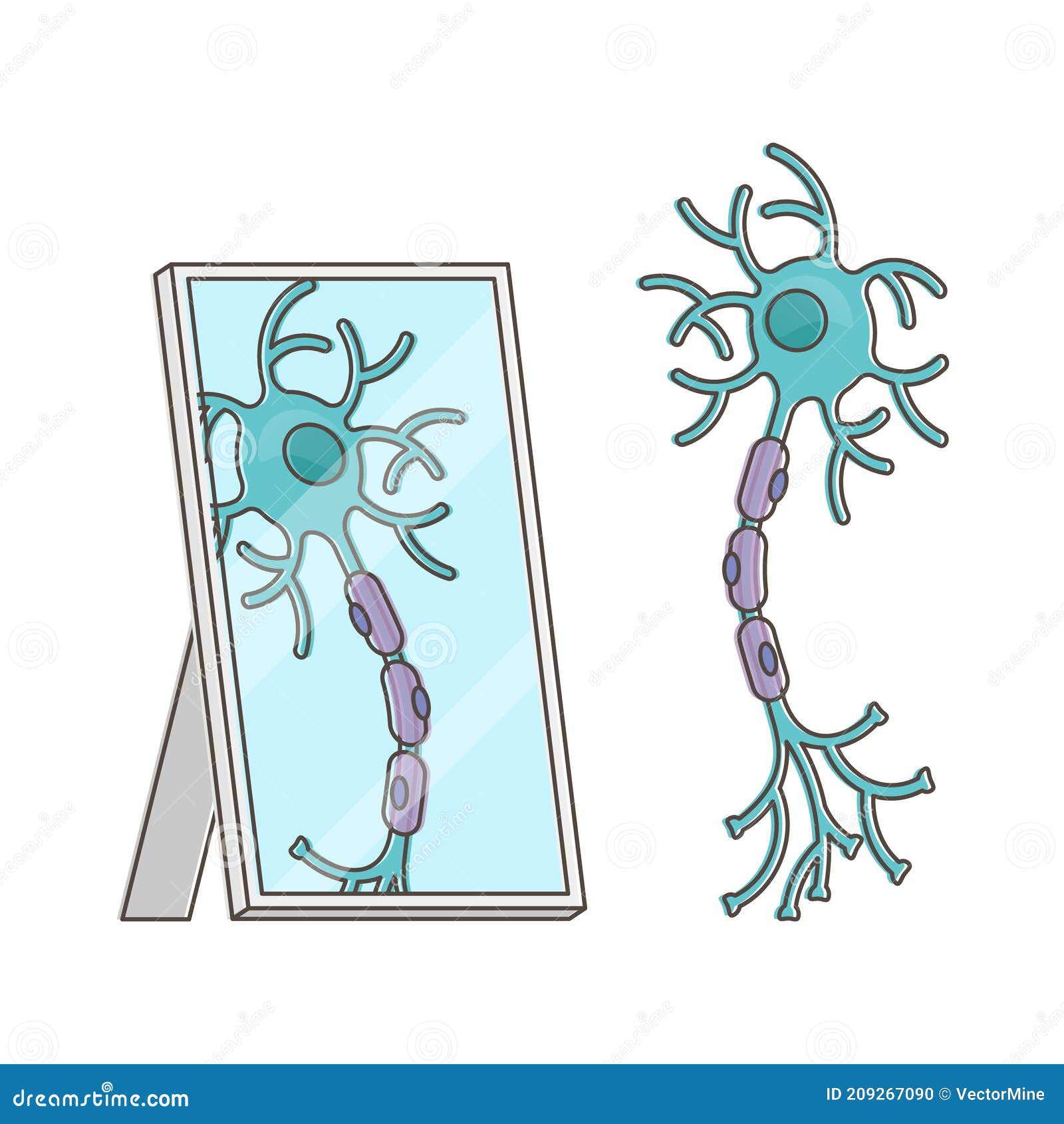
Nerves are bundles of neuron fibers. Nerves run throughout the body. Some nerves, called cranial nerves, run directly to the brain. The rest of the nerves connect with the spinal cord. The nerves in the spinal cord run to and from the brain.
There are two main types of nerves: sensory nerves and motor nerves. Sensory nerves handle information relating to the senses. They send information from the eyes, ears, mouth, nose, skin, and other body parts to the spinal cord and brain. Motor nerves carry messages in the other direction. They send information from the brain and spinal cord to muscles and other body parts.
For example, when a person touches a hot stove, the sensory nerves in the fingers send impulses to the spinal cord. The impulses say that the stove is too hot to touch. The spinal cord then sends impulses through motor nerves to the muscles of the arm. These impulses tell the muscles to pull the arm away from the stove.
Autonomic nerves are a special type of motor nerve. These nerves control the organs inside the body. They regulate breathing, heartbeat, body temperature, the digestive system, and other activities.

Many injuries and diseases can affect the nervous system. Damage to the spinal cord can lead to paralysis. When a person is paralyzed they cannot move. Paralysis happens because the damaged nerves block messages that tell the muscles to move. Multiple sclerosis and poliomyelitis are diseases that attack nerves. Alzheimer’s disease and Parkinson’s disease destroy neurons in the brain. Meningitis is a swelling of the thin coverings around the spinal cord and brain.